WWW.WA
S.ORG
WWW.WA
S.ORG
•
WORLD AQUACULTURE
•
DECEMBER 2014
11
T
he expansion of Philippine aquaculture is essential to
addressing poverty and food insecurity in the midst of a seemingly
irreversible decline in national capture fisheries. Concomitant with
its rise, however, are compounding environmental problems caused
by climate change, lackluster governance and irresponsible farming
practices. It is equally important to ensure aquaculture sustainability
so that fish demand from a rapidly growing population is continually
met and that fish farmers’ socioeconomic well-being is secured.
As such, programs have been developed that aim to enjoin the
government and private sectors with fishing communities to realize
this goal.
Contribution of the Fishery Sector to the
Philippine Economy
The Philippines is a tropical, archipelagic country comprised of
7,107 islands located in Southeast Asia. Surrounded by the Pacific
Ocean on the east, the Celebes Sea and Bornean waters on the south
and the South China Sea on the west and north (Bautista 2009),
it has a total territorial water area of 2,200,00 km
2
while the total
land area covers only about 300,000 km
2
. Its 17,460 km coastline
spans marine areas that include coral reefs, seagrass and algal beds.
In the interior of landmasses are freshwater and brackishwater
A Fish Farmer’s Role
in Sustainable Aquaculture:
An Overview of Philippine Aquaculture
Jonni Fay C. Teves and Janice A. Ragaza
( C O N T I N U E D O N P A G E 1 2 )
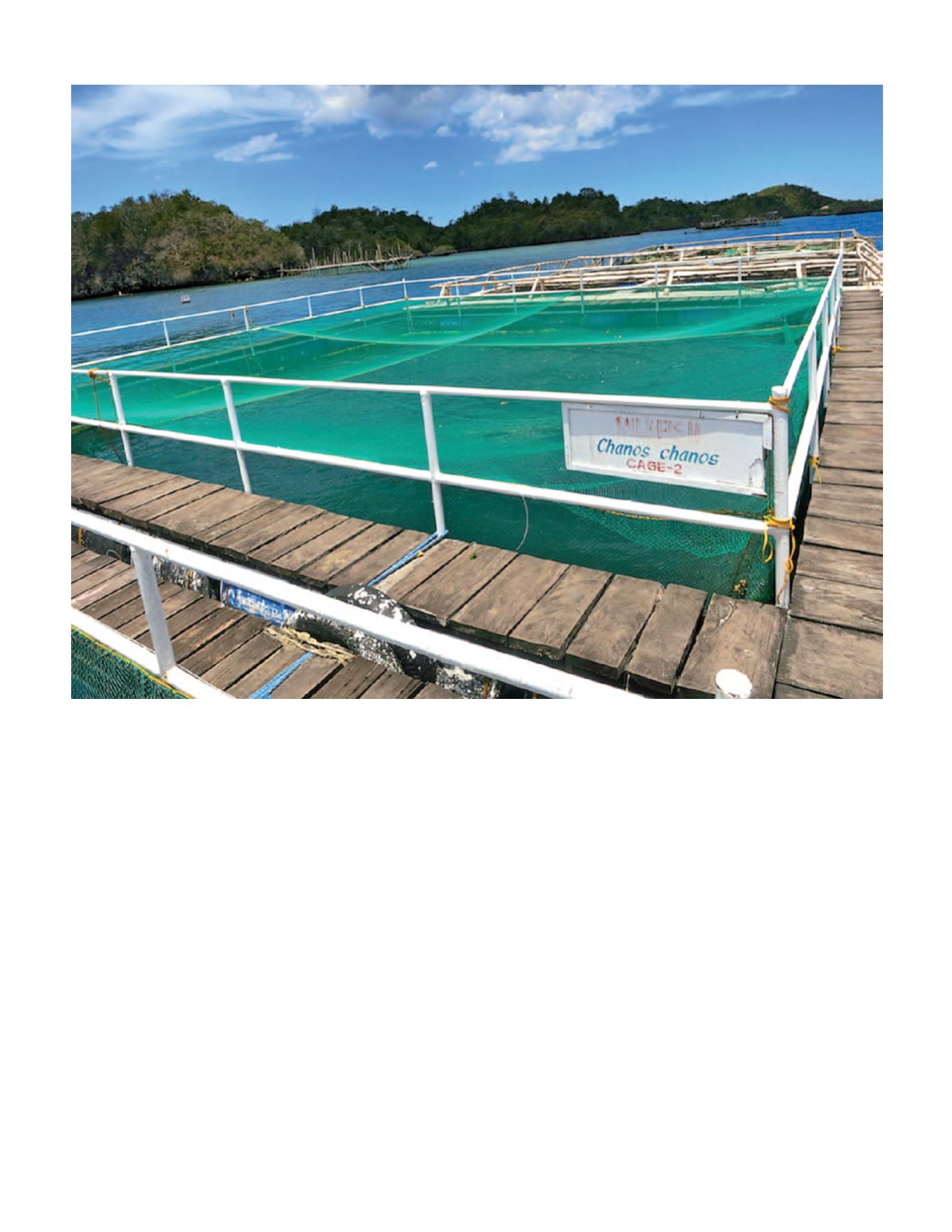
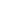
Milkfish culture in cages at SEAFDEC/AQD, Igang marine station, Guimaras, Philippines. Photo by J.A. Ragaza.