ASPECTS OF IMPACT OF PROPOSED BADAGRY DEEP SEA PORT ON THE ECOSYSTEM AND LIVELIHOOD OF FISHING COMMUNITIES IN BADAGRY, LAGOS STATE, NIGERIA
Federal government of Nigeria, in collaboration with Lagos State Government proposed development of a seaport in Badagry.
Badagry is within
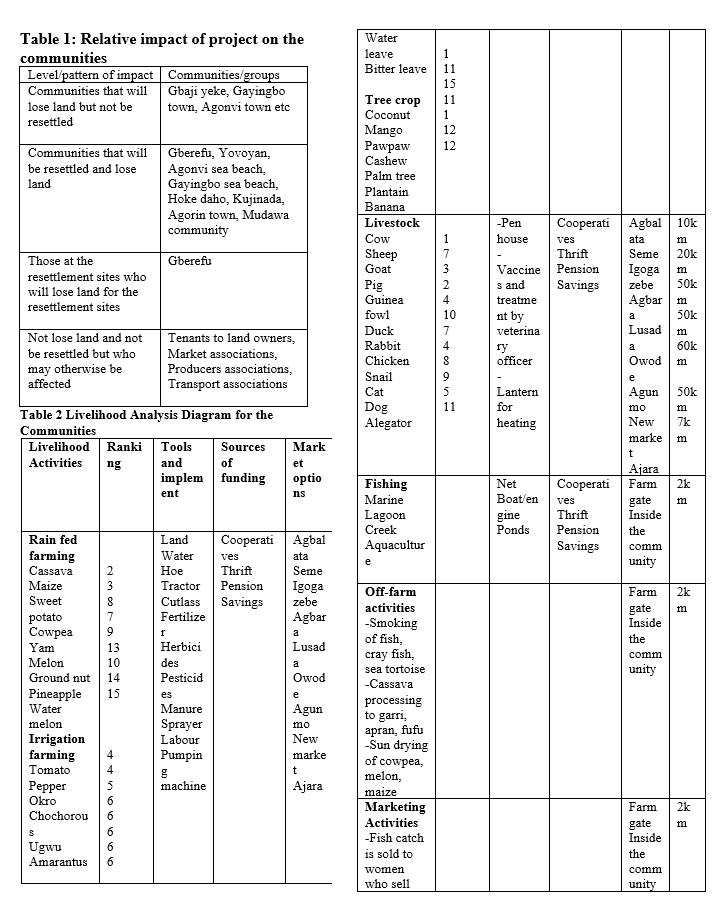
coordinates 6025N 2053/ 6.420670N 2.880 E. It shares boundaries with Ogun State both in the North and in East and is bounded on the west by the Republic of Benin. In the South, it stretches for 180 kilometers along the coast of the Atlantic Ocean.The research examined and documented the current state of the ecosystem and livelihood of thirteen communities that will be impacted by the proposed deep-sea port. The communities that will be impacted are Gberefu , Yovoyan , Gayingbo , Agonvi ,
Agonrin , Hoke-daho , Kujinada , Aivoji , Asakpo , Sheik modawa , Agonvi town, Ganyingbo town and Gbaji
yeke tome.
Qualitative and quantitative approaches were used for the study. Review of secondary data was used to investigate the demographic data of the community. Participatory Rural Appraisal were conducted for about 300 households in the communities.
Majority of the sampled respondents were in the age range of 4 5 years and above with females (60%) more than males (40%) in the entire population sampled. Educational levels are relatively low
among the population sampled. About 65% of the farmers in the communities have primary school education but educational level of their children is very high and 67% of them have attained tertiary level education while 33% have attained secondary level education. The majority of the sampled households are food secured as they have multiple livelihood systems that keep them engaged throughout all seasons of the year. Seventy three livelihood were encountered but capture fisheries is the major occupation in the study area and it is complemented with culture fisheries. Most commonly produced livestock are pig, cow , goat, chicken and duck. Major sources
of income in the communities are fishing and farming followed by artisans , trading and paid jobs. In addition, some activities are gender and age related such as: Hawking (boys and girls) , Fish Smoking(women) , Mart weaving (women),Pap (eko) leaves (women) , Marketing of fish(women) , Vigilante groups
(odua people congress) , Non farming activities (youth, men and women) , Farming (men and women),Livestock (men and women),Sand mining (youth).
Existing groups were not strong enough to control market or operate as pressure group to influence policies and regulate market prices, which has been identified as a major limitation in the study area. There was no regular training or capacity building, hence the groups were not operating as a business enterprise and could not expand or increase capacity. Consequently not able to contribute significantly to poverty alleviation and increase employment opportunities in their localities. This document will serves as one of the guides to government for decision-making and compensation to the communities.