MAXIMIZING TARO Colocasia esculenta L. CORM PRODUCTION IN AQUAPONICS THORUGH MANIPULATION OF WATER QUALITY LATE IN THE VEGETATIVE GROWTH STAGE
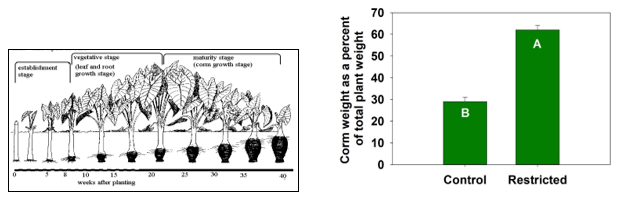
Aquaponics has been widely adopted in Hawaiian communities as a culturally relevant method of home food production. Taro (Kalo in Hawaiian) is a traditional Hawaiian staple crop that does well vegetatively in aquaponics, but does not produce corms of commercially acceptable size. As part of a larger community driven project (malamaaquaponics.org), we tested the hypotheses that low kalo corm yields were due to excessive water nitrogen levels late in vegetative development that hinders corm development. The kalo cultivar 'Maui Lehua' was planted in a randomized complete design with six replications in specially designed dual- tub systems that allowed for the application of two treatments: 1) fish effluent supplied throughout 8 months of plant development (control) and 2) Fish effluent restricted from the system at 4 months and fresh water supplied for the remaining 4 months of development (restricted). The ratio of corm to total biomass is a key indicator of plant maturity. Control plants produced significantly more biomass than restricted plants. Restricted plants had significantly more biomass partitioned to the corm (62% of total biomass) relative to control plants (22% of total biomass). This suggests that we were partially successful in transitioning photosynthate partitioning to the corm. However, individual weights of the primary corm were statistically similar between treatments (376-406g·plant-1). This is still low compared to recorded yields in terrestrial systems (>1kg). Modifications to the system are being made to address observed deficiencies in potassium and iron in plants of both treatments, and total time to harvest will be increased.