IMPACTS OF COVID-19 ON THE U.S. CATFISH AQUACULTURE INDUSTRY
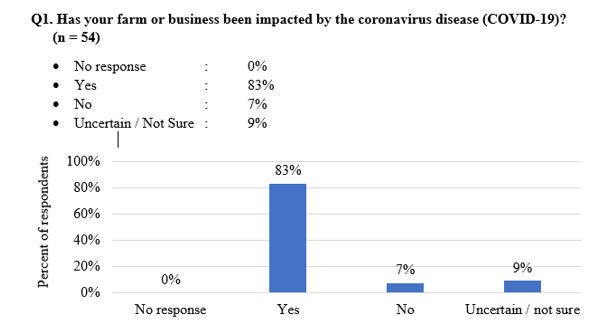
In response to the COVID-19 disease pandemic an effort was launched to assess the impacts on U.S. aquaculture producers. As the largest sector of U.S. freshwater aquaculture, the catfish industry was a critical sector to include in this assessment. A majority (83%) of catfish respondents did report being impacted by the pandemic. The disruption of traditional marketing channels for the catfish industry resulted in loss of revenues reported by 77% of catfish producers. Lost sales reported ranged from $1,001 to more than $1 million. The disruptions and loss of revenue resulted in ripple effects that had subsequent impacts on farm labor and production activities (as well as goods and services) . Eighty-six percent of respondents reported that prices would be reduced as market-sized catfish held in ponds would grow beyond the size that brings a premium price. Catfish respondents to the surveys indicated challenges with labor; ranging from terminations to disruptions in labor due to illness or fear of illness. Producers also reported anticipated disruptions to production activities that would follow farms for the 2-year product cycle. Comments submitted by producers noted increased costs for production inputs, particularly feed.
This presentation will cover the findings regarding the i mpacts of COVID-19 on U.S. catfish a quaculture businesses.