METAANALYSIS OF DUCKWEED AS AN ALTERNATIVE FEED FOR FINFISH AQUACULTURE
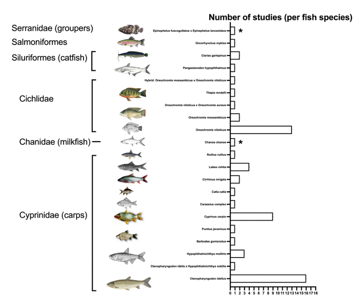
One of the primary sustainability challenges in aquaculture is replacing fish meal with plant based ingredients in aquafeeds. Plant based feeds often suffer with lower crude protein percentages and can cause dysbiosis in the fish gut microbiomes leading to suboptimal performance during growout. Duckweed (Lemneaceae ) is a family of aquatic plants with high protein content and has been used successfully for various types of terrestrial livestock and fish feed. In this systematic review and meta analysis of 51 papers, we summarize the extent by which duckweed has been used in fish production including the species of fish tested, the growout stage of fish, method of application, and the countries where duckweed are endemic. Duckweed studies spanned a total of 17 species of fish (15 freshwater and 2 marine) which collectively are valued at 263 billion USD annually, and comprise 28% of total aquaculture production by mass. The average experiment length was 76 days (S.D. 44) with most fish at the fingerling life stage. Duckweed was fed to the fish either directly or allowed to graze on fresh growth, dried, as a fertilizer to the ponds, or fermented with newer studies opting for dried feed formulation. The most common formulation other than 100% was 20%. We performed an analysis of impacts of growth across 13 studies on tilapia. Of duckweed species used in experiments, the Lemna spp were the most common with L. minor and L. gibba most consistent. Wolffia arrhiza and Spirodela polyrrhiza were also more commonly used in experiments. The majority of duckweed species, especially from Wollfiella have not been tested as a fish feed. Future research should aim to describe methods of removing or mitigating heavy metal toxicity and anti-nutrients from duckweed. We hypothesize three opportunities to detoxify duckweed including 1) genetic engineering of the plant, 2) microbial treatments of feed stock prior to feed formulation, and 3) designing gut probiotics to enable fish to detoxify compounds in-vivo.