EFFECTS OF FERMENTED CORN PROTEIN CONCENTRATE TO REPLACE FISHMEAL IN PRACTICAL DIETS FOR PACIFIC WHITE SHRIMP Litopenaeus vannamei
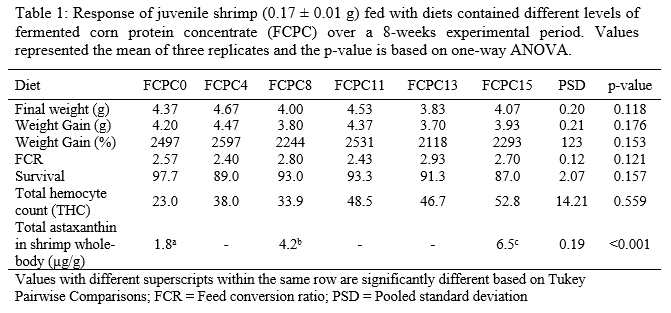
One of the latest corn-based ingredients available in the market is a fermented corn protein concentrate (FCPC), which is expected to perform well in shrimp diets due to its nutritional profile and the probiotic properties of fermented products. The current study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy FCPC as a replacement for fish meal (FM) in practical diets of pacific white shrimps, Litopenaeus vannamei. Graded levels of FCPC (0, 4, 8, 11, 13, and 15 g/kg) were used to replace fishmeal (16, 12, 8, 4, 2, and 0 g fishmeal/kg) in the diet, which was evaluated over a 8 weeks growth trial (initial weight 0.17±0.01 g; n=3). At the conclusion, no significant differences were detected in growth, FCR, survival, or hematological parameters of shrimp (P-value>0.05). Results reveals the efficacy of FCPC to replace 100% fishmeal at an inclusion level as high as 15%, without compromising the performances of shrimp. Significant increase (p-value<0.001) in total hemocyte count (THC) and astaxanthin level in shrimp noted in respond to the inclusion level of FCPC (based on regression analysis) assumed to be due to the probiotic properties of fermented corn extractives in product and due to the availability of bio-convertible carotenoids in FCPC, respectively (Table 1).