FACTORS TRIGGERING DISEASE OUTBREAKS IN AQUACULTURE PRODUCTION SYSTEMS
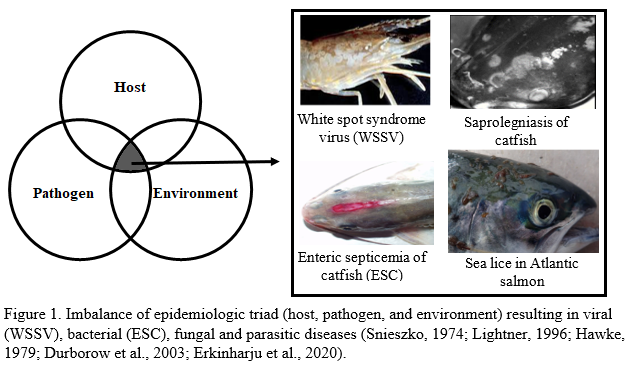
In recent years, t he adoption of intensive production practices ha s tremendously increased aquaculture production. However, with intensification comes added pressure on production systems, which often leads to infectious disease outbreaks. The pathogens causing diseases in aquaculture production systems are primarily categorized as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. The dynamic interactions of the elements constituting the epidemiologic triad namely host, pathogen, and the environment are key to disease outbreaks in any system (Figure 1) . Citing reported cases, this retrospective review explored the subfactors of each key element and how the complex interplay among them might have contributed towards disease outbreaks in production systems . Factors discussed here include pathogen virulence, host-specificity, mutations, transmission routes, mechanisms of infection, methods of interaction, vectors, co-infections , stress, and sub-optimal environmental parameters off-balancing the epidemiologic triad. Proactive methods to e nhance the health of the aquaculture species and biosafety measures to prevent the spread of infectious diseases are also mentio ned. In nutshell, t his review covers the epidemiological triad and their associated factors, the imbalance of which directly or indirectly culminate in disease outbreaks . It also discusses potential management aspects such as vaccination and biosecurity measures to minimize disease incidences.